In the world of printing, the final touch can make all the difference. Many people often consider lamination a critical finishing process that not only protects printed materials but also significantly enhances their visual appeal. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of what is lamination in printing, from its definition and various types to its numerous benefits and wide-ranging applications.
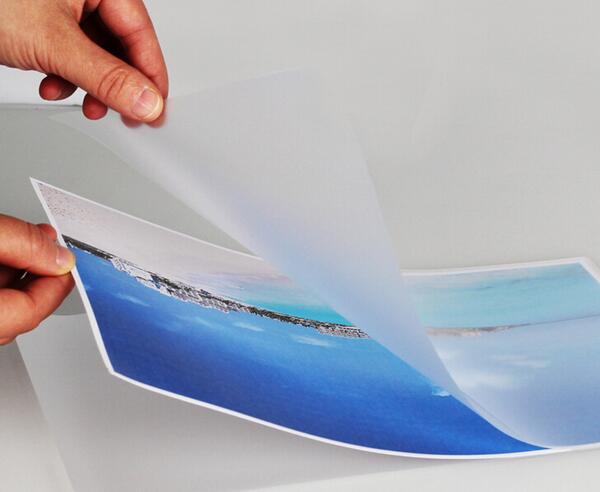
Understanding What is Lamination in Printing
Lamination in printing is defined as the process by which a thin, transparent layer is applied to the surface of a material, such as paper or stickers, to protect it and enhance its appearance. Additionally, this involves adding a clear plastic film to one or both sides of a printed item. For instance, laminating materials gives them an extra shield against everyday wear.
Types of Lamination for Printed Materials
The printing and packaging industries use several common types of lamination. Moreover, they are typically categorized by their final appearance and the method of application.
Based on Finish
- Glossy Lamination: This finish is provided with a shiny, reflective surface that makes colors appear brighter and more vibrant. Furthermore, it is frequently chosen as an excellent option for promotional materials like brochures and posters.
- Matte Lamination (Doff): This finish offers an elegant and exclusive feel by creating a smooth, non-shiny surface. In addition, it is commonly used for high-end items such as business cards, book covers, and premium packaging.
Based on Application Method
- Hot (Thermal) Lamination: This method uses heat to activate an adhesive on the lamination film, bonding it securely to the surface of the printed media. The process involves operators feeding the material between heated rollers, where the system applies pressure to ensure a strong seal.
- Cold Lamination: This method uses a pressure-sensitive adhesive to bond the film to the media without heat. Therefore, many consider it the ideal choice for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures.
The Key Benefits of Lamination in Printing
Lamination offers numerous advantages for your printed materials:
- Protection: It safeguards prints from damage caused by water, dust, scratches, and UV rays.
- Professional Appearance: Lamination adds a glossy or matte effect, enhancing the aesthetic of any item and making it look more appealing and professional.
- Enhanced Durability: It extends the lifespan of printed media by preventing physical wear and tear.
- Ease of Cleaning: You can easily wipe laminated surfaces clean of smudges and dirt.
The Lamination Process Explained in Detail
Several key steps ensure a high-quality lamination result:
- Preparation: First, make sure the surface of the printed media is clean and dry.
- Selection: Choose the appropriate type of lamination, whether glossy or matte, hot or cold, based on the project’s requirements.
- Application:
- Hot Lamination: Place the printed item between sheets of laminating film and feed it into a thermal laminating machine where heat and pressure bond the layers.
- Cold Lamination: Position the media between layers of cold lamination film and run it through a cold-laminating machine or press it manually to create a secure bond.
- Finishing: Trim any excess plastic film from the edges to achieve a clean, professional finish.

Wide-Ranging Industry Applications of Lamination
Various sectors extensively use lamination for a wide range of applications:
- Printing: Products like brochures, business cards, posters, and book covers are protected and beautified through this process.
- Packaging: An extra layer of protection is added to product packaging, making it more durable and attractive to consumers.
- Important Documents: Documents such as certificates, diplomas, and ID cards are preserved from damage and forgery.
- Stickers and Labels: It maintains print quality and extends the lifespan of stickers used for branding or product information.
Tips for Choosing the Right Type of Lamination for Your Needs
To achieve the best results, consider the following factors:
- Media Type: Match the lamination to the material and the intended purpose of the printed item.
- Budget: Factor lamination costs into your production budget. While thermal lamination may require a higher initial investment in machinery, cold lamination often serves as a more budget-friendly alternative.
- Aesthetic Goals: Choose between a glossy or matte finish based on the desired final appearance.
- Required Durability: Evaluate the protection your printed item needs based on its intended use and the conditions it will face.
Conclusion
In summary, the printing and packaging industries recognize lamination as an essential process that offers a perfect blend of protection and aesthetic enhancement. By understanding the different types, benefits, and processes involved in lamination, you can make an informed choice that ensures your final product is both durable and visually impressive.
